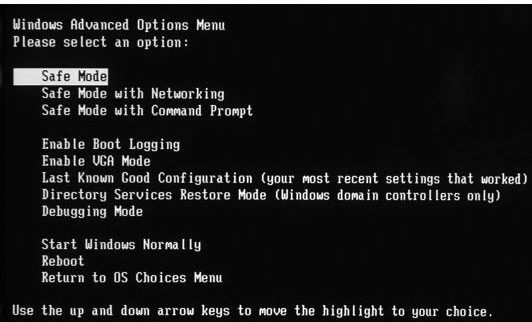
Users who are running later versions of Windows will get different options for different versions of Safe Mode. For example, you may have options for “Safe Mode”, “Safe Mode with Networking”, and “Safe Mode with Command Prompt.” Below is a brief description of each of these different modes.
- Safe Mode
The basic Safe Mode option is usually what most users will want to choose when troubleshooting their computer. This is the most basic Safe Mode option and has no additional support. - Safe Mode with Networking
For users needing access to the Internet or the network they’re connected to while in Safe Mode, users may want to choose this option. This mode is helpful for when you need to be in Safe Mode to troubleshoot, but also need access to the Internet so you can get updates, drivers, or other files to help troubleshoot your issue. - Safe Mode with Command Prompt
This Safe Mode allows you to have access to the command line (MS-DOS prompt).